Understanding Upper Abdominal Pain Causes and Remedies

Navigating Upper Abdominal Pain: Understanding and Management
Understanding Upper Abdominal Pain
Upper abdominal pain can be a perplexing and uncomfortable experience for many individuals. It refers to discomfort or sensations of pain felt in the area between the lower rib cage and the umbilicus (belly button). While it may arise from various causes, understanding the underlying factors contributing to upper abdominal pain is crucial for effective management.
Common Causes of Upper Abdominal Pain
A myriad of factors can lead to upper abdominal pain, ranging from benign conditions to more serious medical issues. Some common causes include gastrointestinal problems such as indigestion, acid reflux, gastritis, and peptic ulcers. Additionally, issues related to the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys can also contribute to upper abdominal discomfort.
Symptoms and Presentation
The presentation of upper abdominal pain can vary widely depending on the underlying cause. Individuals may experience sensations of burning, cramping, bloating, or sharp stabbing pain in the upper abdomen. Other accompanying symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, loss of appetite, and fever. Understanding these symptoms can help narrow down potential causes and guide appropriate management strategies.
Diagnostic Evaluation
Diagnosing the cause of upper abdominal pain often requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. This typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as blood tests, imaging studies (e.g., ultrasound, CT scan), and endoscopic procedures (e.g., upper endoscopy, colonoscopy). These diagnostic tools help identify the underlying pathology and guide treatment decisions.
Management and Treatment
The management of upper abdominal pain depends on its underlying cause. For conditions such as indigestion or acid reflux, lifestyle modifications (e.g., dietary changes, weight management) and over-the-counter medications (e.g., antacids, proton pump inhibitors) may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms. In cases of more serious conditions such as gallstones or pancreatitis, medical
Conquering Ulcers Strategies for Relief and Healing

Understanding Ulcers: A Comprehensive Guide
Ulcers are a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. From the discomfort they cause to the potential complications they pose, understanding ulcers is essential for effective management and treatment. In this article, we delve deep into the world of ulcers, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
The Root Causes of Ulcers
Ulcers typically develop when the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus becomes damaged. This damage can occur due to various factors, including infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria, long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and stress. While these factors can increase the risk of developing ulcers, each individual’s susceptibility may vary based on their genetics, lifestyle, and overall health.
Recognizing the Symptoms
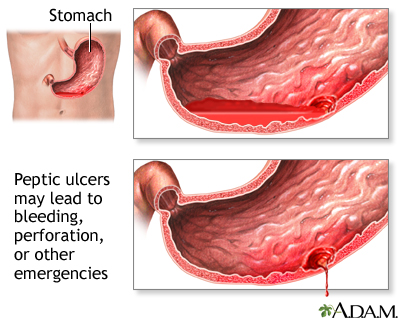
Symptoms of ulcers can vary depending on their location and severity. Common symptoms include a burning or gnawing pain in the abdomen, particularly between meals or at night, bloating, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, and loss of appetite. In some cases, ulcers can cause more serious complications, such as bleeding, perforation of the stomach or intestine, or obstruction of the digestive tract. It’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms suggestive of an ulcer.
Diagnosing Ulcers: What to Expect
Diagnosing ulcers typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your healthcare provider may inquire about your symptoms, lifestyle habits, and medical history to better understand your condition. They may also perform a physical examination to assess for signs of ulcers, such as tenderness or bloating in the abdomen. Additionally, diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, X-rays, blood tests, or stool tests may be recommended to confirm the presence of an ulcer and determine its severity.
Treatment Approaches for Ulcers
Treatment for